👨💻 TIL
TIL6 - 2023.09.26
zunwon
2023. 9. 26. 18:56

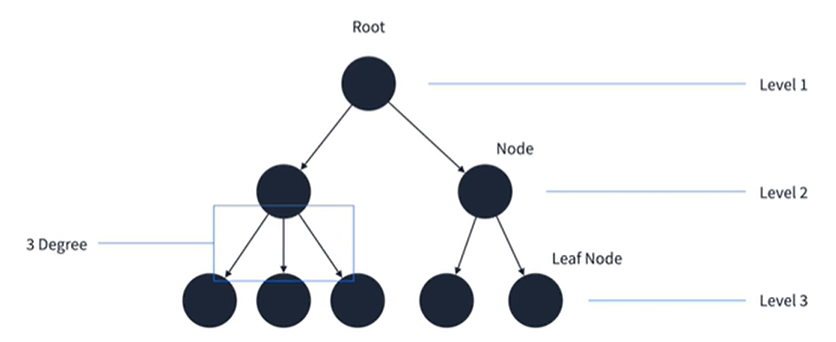
트리 (Tree)
- 방향 그래프의 일종으로 하나의 루트에서 하위로 뻗어나가는 구조를 가지고 있다
- 루트(Root) : 가장 상위에 존재하는 정점
- 노드(Node) : 각 정점
- 리프 노드(Leaf Node) : 자식이 없는 노드
- 레벨(Level) : 루트로부터 몇 번의 깊이
- 차수(Degree) : 한 정점에서 뻗어나가는 정점의 수
- 인접 행렬, 인접 리스트로 구현 가능
- ex) 부서, 디렉토리 구조
트리의 특징
- 루트 정점을 제외한 모든 정점은 반드시 하나의 부모 정점을 가진다
- 정점이 N개인 트리는 반드시 N-1개의 간선을 가진다
- 루트에서 특정 정점으로 가는 경로는 유일하다
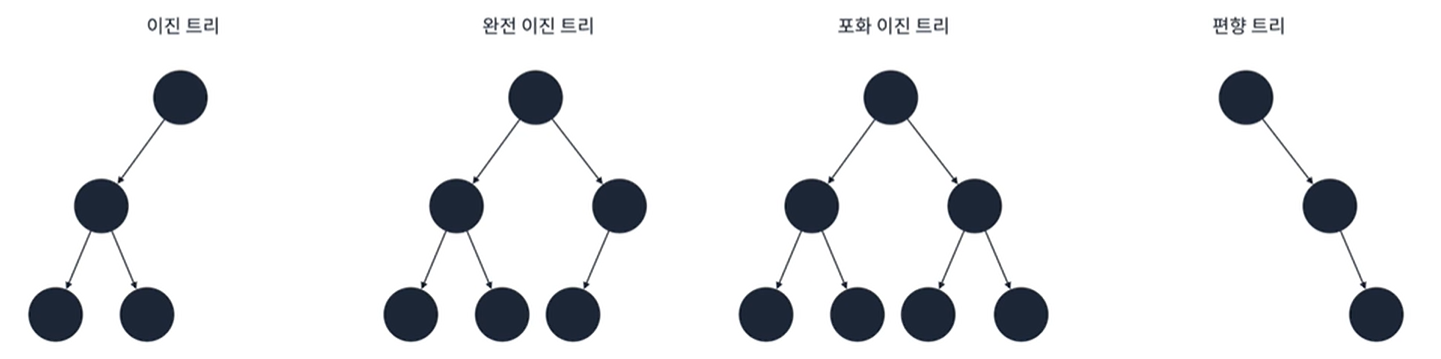
이진 트리
- 각 정점이 최대 2개의 자식을 가지는 트리를 의미한다
이진 트리의 특징
- 정점이 N개인 이진 트리는 최악의 경우 높이가 N이 될 수 있다 ➜ N개의 정점을 가진 편향 트리
- 정점이 N개인 포화 또는 완전 이진 트리의 높이는 logN이다
- 높이가 h인 포화 이진 트리는 2^h - 1개의 정점을 가진다
- 이진 탐색 트리, 힙, AVL 트리, 레드 블랙 트리
이진 트리 구현
- 배열
// 0번 인덱스는 관리를 위해 비워둔다.
// Left = Index * 2
// Right = Index * 2 + 1
// Parent = floor(Index / 2)
const tree = [
undefined,
// 1
9,
// 1+2, 1+2+1
3, 8,
// 2+2, 2+2+1, 3+2, 3+2+1
2, 5, undefined, 7,
// 4+2, 4+2+1, 5+2, 5+2+1
undefined, undefined, undefined, 4
]- 연결 리스트
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class Tree {
contructor(node) {
this.root = node;
}
display() {
// Level Order
const queue = new Queue();
queue.enqueue(this.root);
while (queue.size) {
const currentNode = queue.dequeue();
console.log(currentNode.value);
if (currentNode.left) queue.enqueue(currentNode.left);
if (currentNode.right) queue.enqueue(currentNode.right);
}
}
}
const tree = new Tree(new Node(9));
tree.root.left = new Node(3);
tree.root.right = new Node(8);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.left.right.right = new Node(4);과제
전위 / 중위 / 후위 순회 (스택) 검색하여 직접 구현
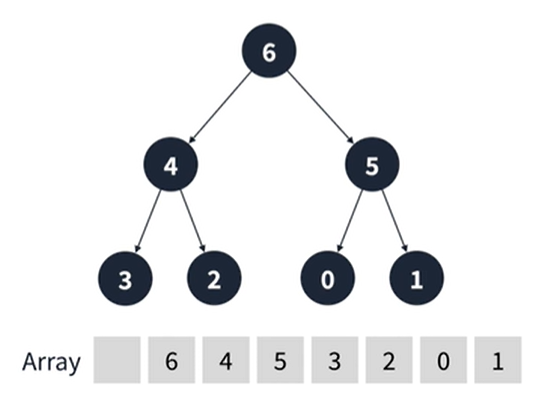
힙(Heap)
이진 트리 형태를 가지며 우선순위가 높은 요소가 먼저 나가기 위해 요소가 삽입, 삭제 될 때 바로 정렬되는 특징이 있다
힙의 특징
- 우선 순위가 높은 요소를 루트(Root)로 배치하고 루트가 먼저 나가는 특징을 가진다
- 루트가 가장 큰 값이 되는 최대 힙(Max Heap)과 루트가 가장 작은 값이 되는 최소 힙(Min Heap)이 있다(오름차순, 내림차순의 차이)
- 아쉽게도 자바스크립트에서 직접 구현해야 한다
힙 요소 추가 알고리즘
- 요소가 추가될 때는 이진 트리의 가장 마지막에 추가한다
- 추가 후 부모 정점보다 우선순위가 높다면 부모 정점과 순서를 바꾼다
- 이 과정을 반복하면 결국 가장 우선순위가 높은 정점이 루트가 된다
- 요소는 항상 이진 트리의 마지막에 추가되기 때문에 힙은 항상 완전 이진 트리이다
- 높이가 log N이기 때문에 힙의 요소 추가 알고리즘은 O(log N) 시간복잡도를 가진다
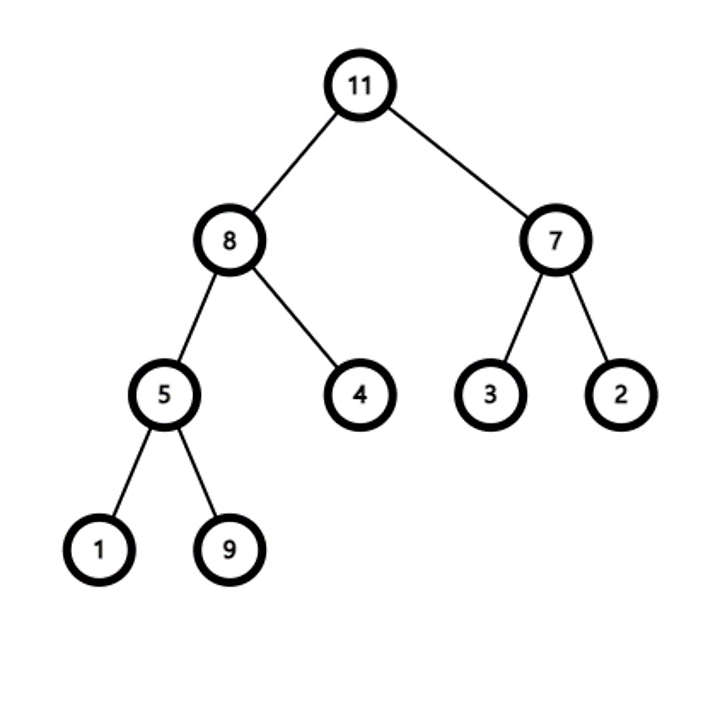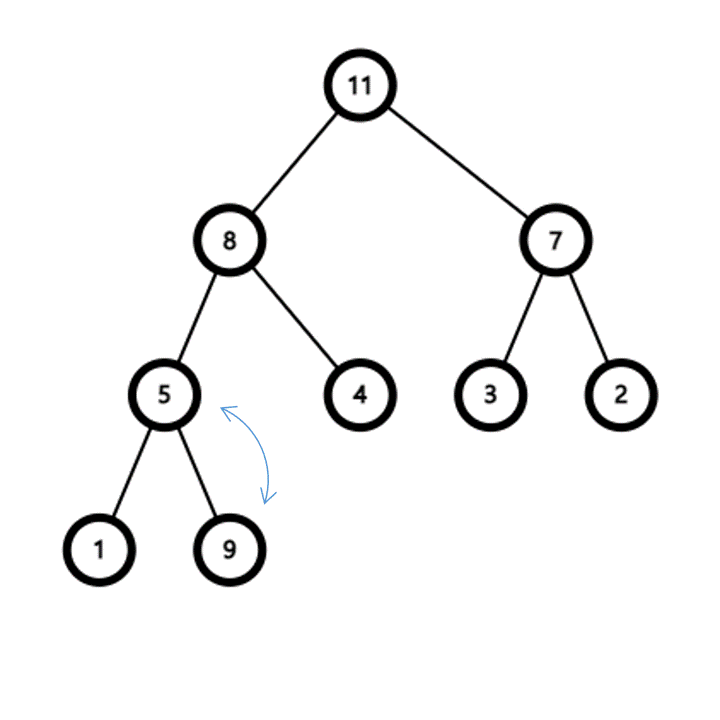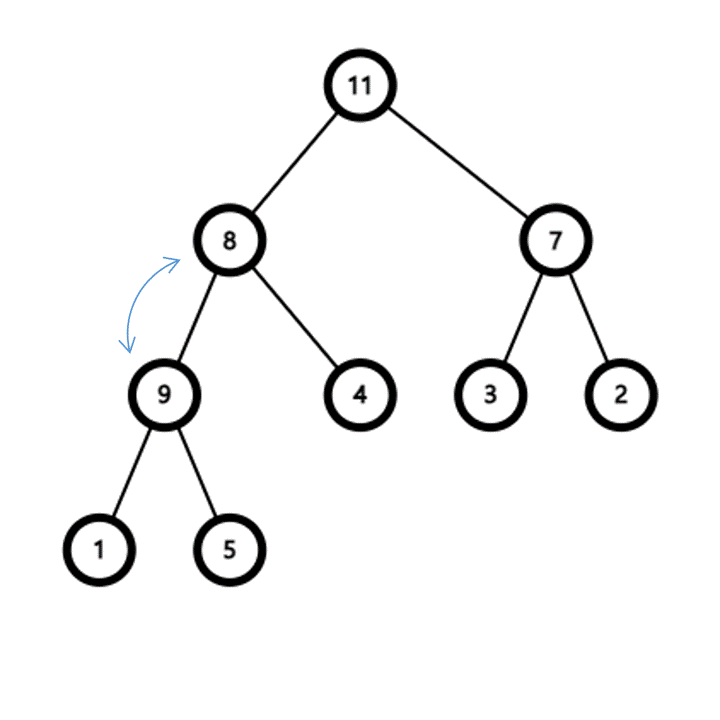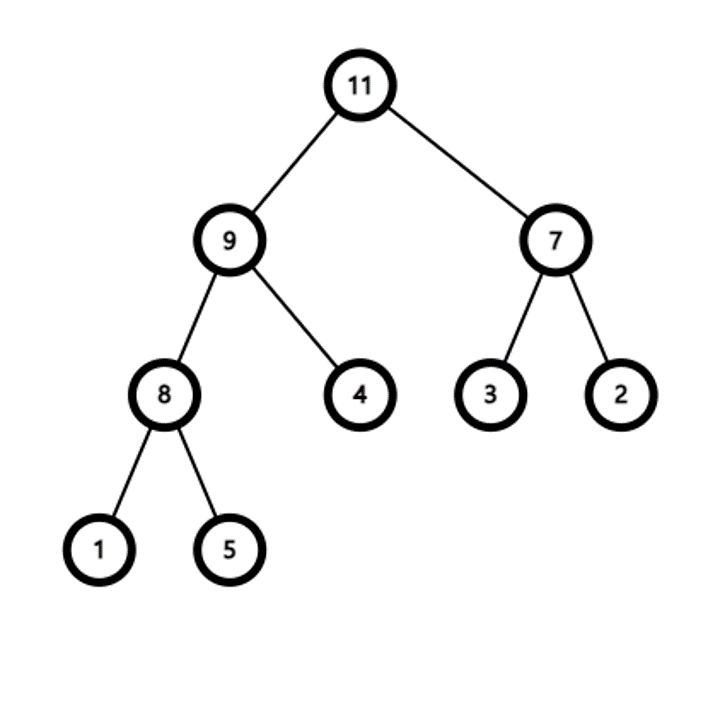
힙 요소 제거 알고리즘
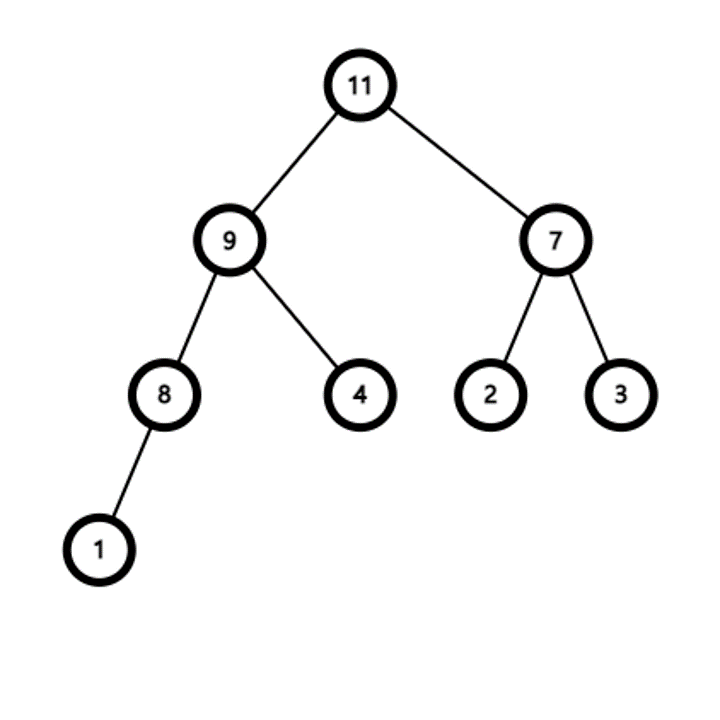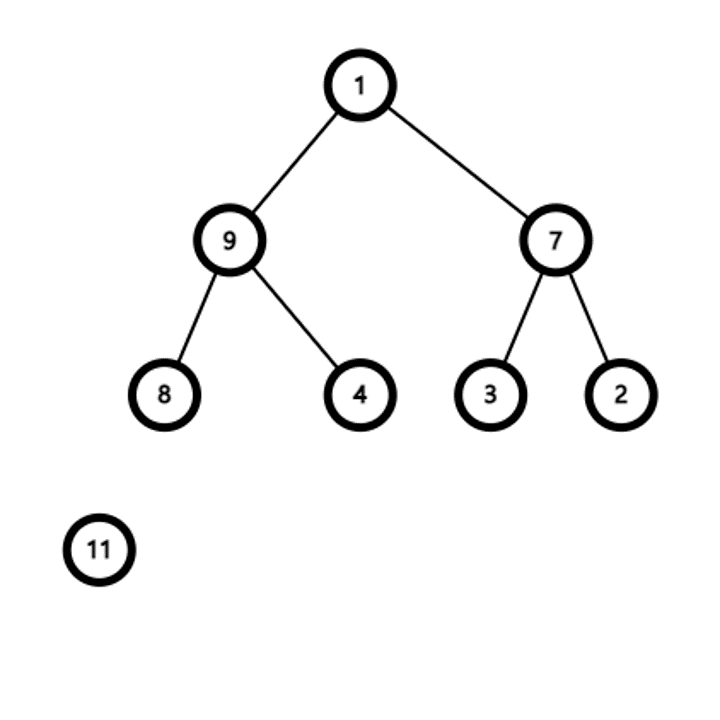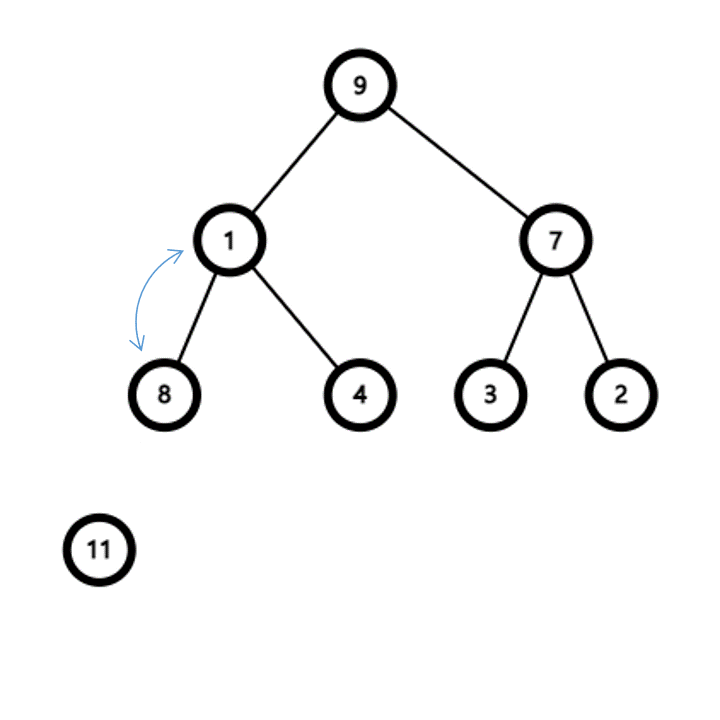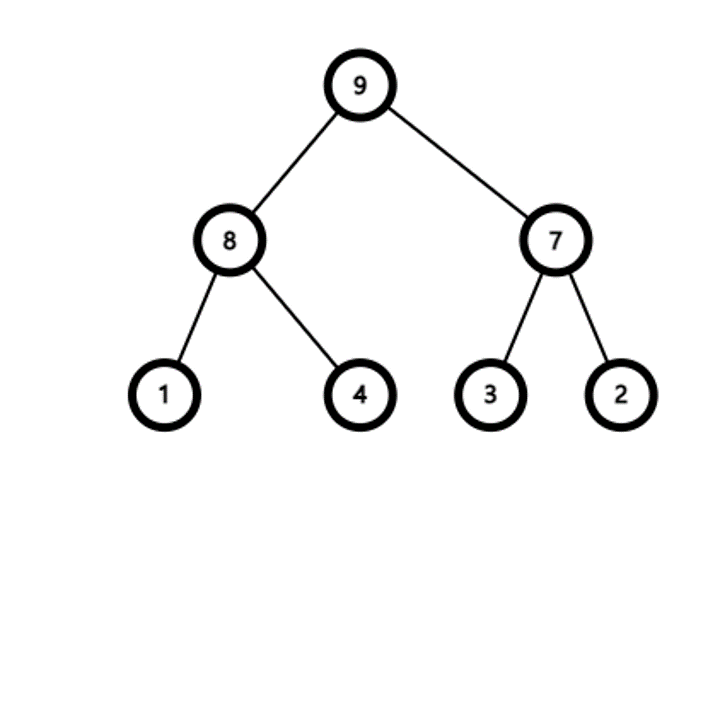
- 요소 제거는 루트 정점만 가능하다
- 루트 정점이 제거된 후 가장 마지막 정점이 루트에 위치한다
- 루트 정점의 두 자식 정점 중 더 우선순위가 높은 정점과 바꾼다
- 두 자식 정점이 우선순위가 더 낮을 때까지 반복한다
- 높이는 log N이기에 힙의 요소 제거 알고리즘은 O(log N) 시간복잡도를 가진다
힙 추가 & 제거 코드 구현
class MaxHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null];
}
push(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
let currentIndex = this.heap.length - 1;
let parentIndex = Math.floor(currentIndex / 2);
while (parentIndex !== 0 && this.heap[parentIndex] < value) {
const temp = this.heap[parentIndex];
this.heap[parentIndex] = value;
this.heap[currentIndex] = temp;
currentIndex = parentIndex;
parentIndex = Math.floor(currentIndex / 2);
}
}
pop() {
const returnValue = this.heap[1];
this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop();
let currentIndex = 1;
let leftIndex = 2;
let rightIndex = 3;
while (
this.heap[currentIndex] < this.heap[leftIndex] ||
this.heap[currentIndex] < this.heap[rightIndex]
) {
if (this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[rightIndex]) {
const temp = this.heap[currentIndex];
this.heap[currentIndex] = this.heap[rightIndex];
this.heap[rightIndex] = temp;
currentIndex = rightIndex;
} else {
const temp = this.heap[currentIndex];
this.heap[currentIndex] = this.heap[leftIndex];
this.heap[leftIndex] = temp;
currentIndex = leftIndex;
}
leftIndex = currentIndex * 2;
rightIndex = currentIndex * 2 + 1;
}
return returnValue;
}
}
const heap = new MaxHeap();
heap.push(45); // 63
heap.push(36); // 54
heap.push(54); // 45
heap.push(27); // 36
heap.push(63); // 27
console.log(heap.heap); // [ null, 63, 54, 45, 27, 36 ]
heap.pop();
heap.pop();
console.log(heap.heap); // [ null, 45, 36, 27 ]과제 : 최소 힙 구현
우선순위 큐
- FIFO인 큐와 달리 우선 순위가 높은 요소가 먼저 나가는 큐
- 우선순위 큐는 자료구조가 아닌 개념이다
트라이 (Trie)
- 문자열을 저장하고 효율적으로 탐색하기 위한 트리 형태의 자료구조
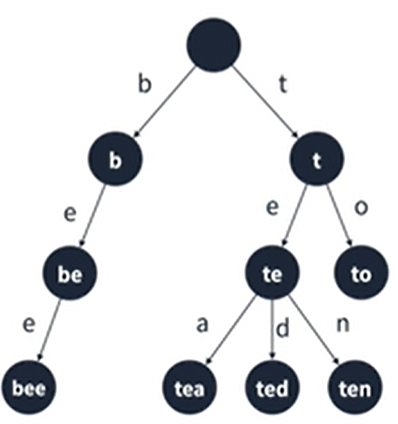
트라이의 특징
- 검색어 자동완성, 사전 찾기 등에 응용될 수 있다
- 문자열을 탐색할 때 단순하게 비교하는 것보다 효율적으로 찾을 수 있다
- 보통 문자열을 탐색할 때 (문자열의 갯수 X 문자열의 길이)만큼 시간이 걸리지만 트라이는 L이 문자열의 길이일 때 탐색, 삽입은 O(L)만큼 걸린다
- 대신 각 정점이 자식에 대한 링크를 전부 가지고 있기에 저장 공간을 더 많이 사용한다는 단점이 있다
트라이 구조
- 루트는 비어있다
- 각 간선(링크)은 추가될 문자를 키로 가진다
- 각 정점은 이전 정점의 값 + 간선의 키를 값으로 가진다
- 해시 테이블과 연결 리스트를 이용하여 구현할 수 있다
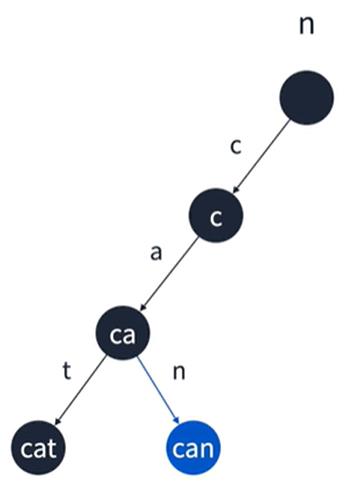
트라이 코드 구현
class Node {
constructor(value ='') {
this.value = value;
this.children = new Map();
}
}
// Node {value: '', children: Map(0)}
class Trie {
constructor() {
this.root = new Node();
}
insert(string) { // string = 'cat'
let currentNode = this.root; // root부터 탐색을 시작한다.
for (const char of string) { // 문자열을 맨 앞부터 문자 하나씩 순회한다. char = 'c'
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) { // 현재 노드가 'c'를 간선으로 가지고 있지 않다면,
currentNode.children.set(char, new Node(currentNode.value + char)); // 새롭게 노드를 추가한다.
// Node {value:'', children: Map(1) {'c' => Node}}
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char); // 그러고나서 char 노드로 이동한다.
// 'c' 간선이 이어진 노드로 이동
// Node {value: 'c', children: Map(0)}
}
}
has(string) {
let currentNode = this.root;
for (const char of string) {
if (!currentNode.children.has(char)) {
return false;
}
currentNode = currentNode.children.get(char);
}
return true;
}
}
const trie = new Trie();
trie.insert('cat');
trie.insert('can');
console.log(trie.has('cat')); // true
console.log(trie.has('can')); // true
console.log(trie.has('cap')); // false정렬 (Sort)
- 요소들을 일정한 순서대로 열거하는 알고리즘
정렬의 특징
- 정렬 기준은 사용자가 정할 수 있다 ( 오름차순 / 내림차순 )
- 크게 비교식과 분산식 정렬로 나눌 수 있다
- 대부분의 언어가 빌트인으로 제공해준다
- 삽입, 선택, 버블, 머지, 힙, 퀵 정렬 등 다양한 정렬 방식이 존재
어떤 정렬이 제일 빠를까??
비교식 정렬
버블 정렬
- 서로 인정합 두 요소를 검사하여 정렬하는 알고리즘
- O(N²) 시간 복잡도를 가진다
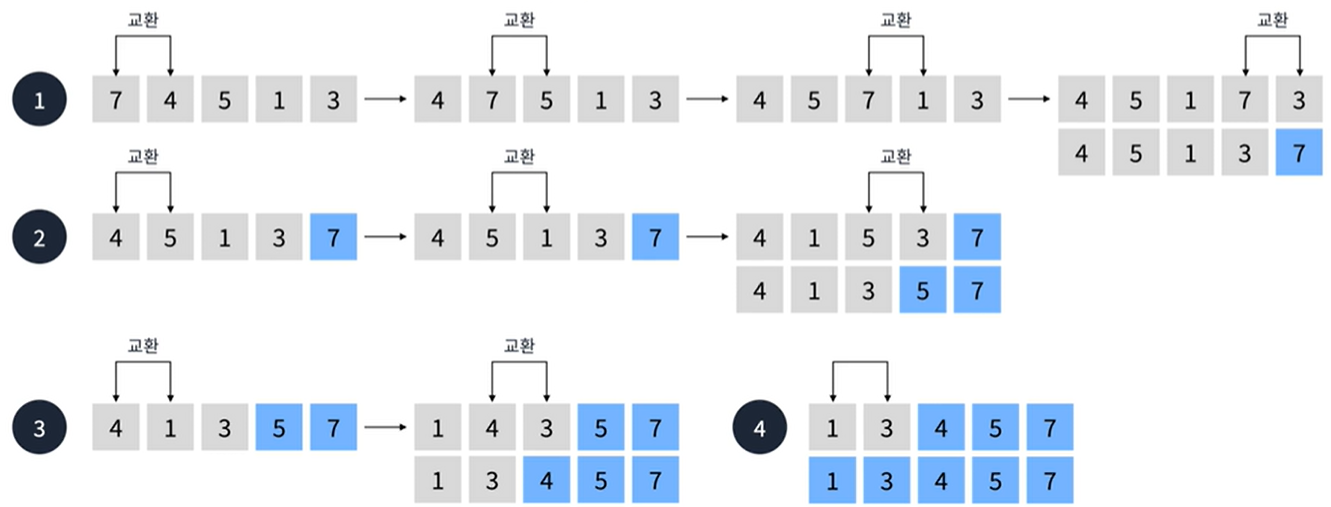
선택 정렬
- 선택한 요소와 가장 우선순위가 높은 요소를 교환하는 정렬 알고리즘
- O(N²) 시간 복잡도를 가진다
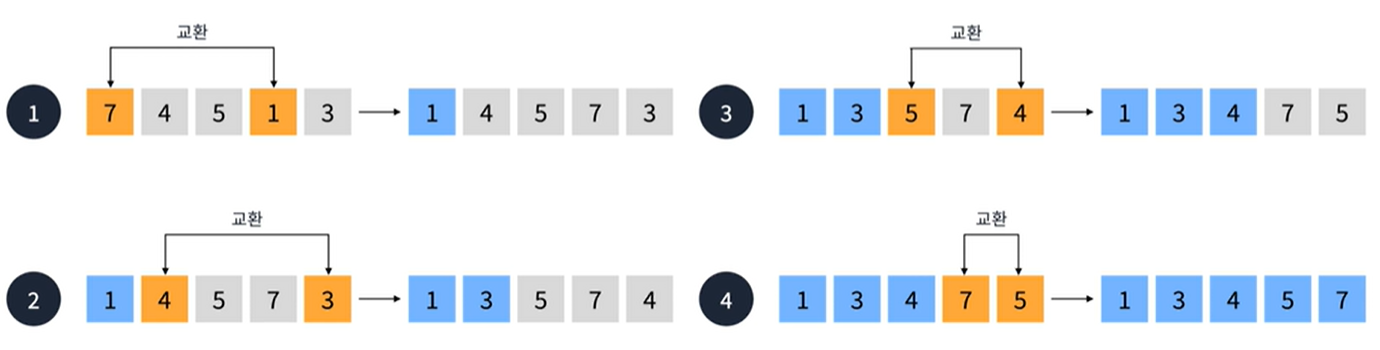
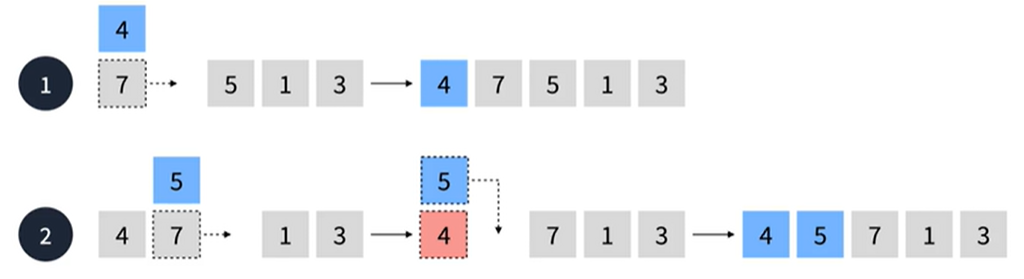
삽입 정렬
- 선택한 요소를 삽입할 수 있는 위치를 찾아 삽입하는 방식의 정렬 알고리즘
- O(N²) 시간 복잡도를 가진다
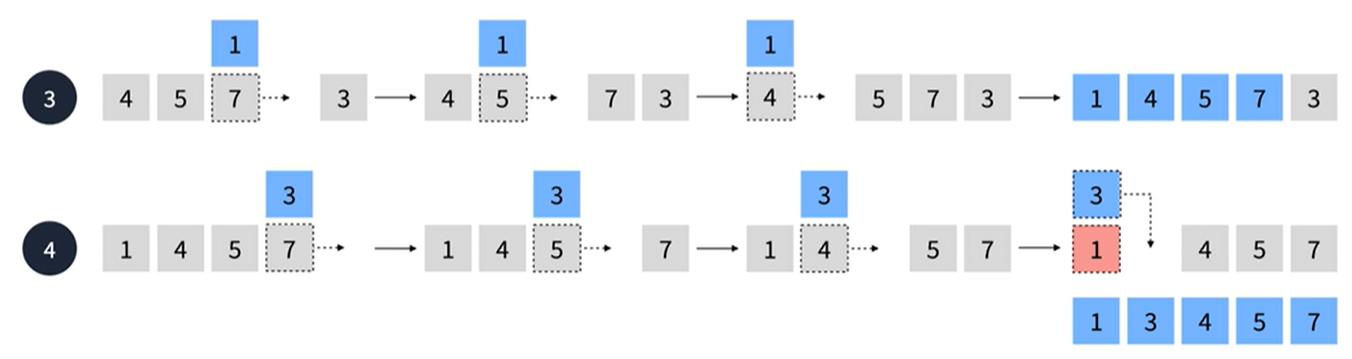
분산식 정렬
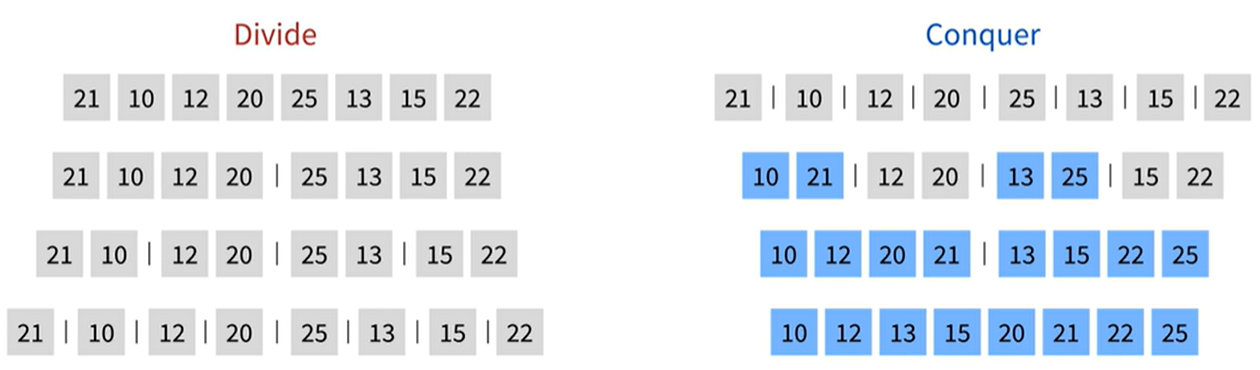
분할 정복
- 문제를 작은 2개의 문제로 분리하고 더 이상 분리가 불가능할 때 처리한 후 합치는 전략

합병 정렬
- 분할 정복 알고리즘을 이용한 최선과 최악이 같은 안정적인 정렬 알고리즘
- O(NlogN) 시간 복잡도를 가진다
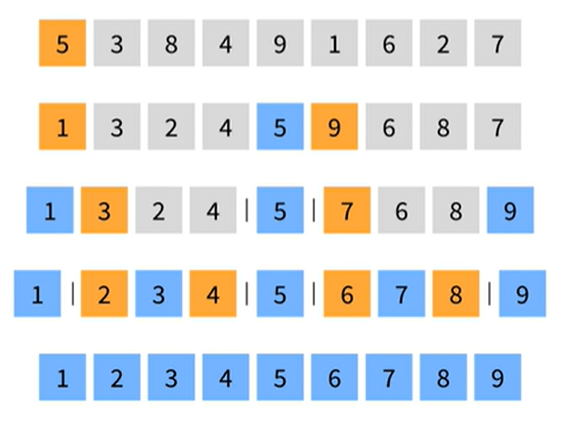
퀵 정렬
- 분할 정복 알고리즘을 이용한 매우 빠르지만 최악의 경우가 존재하는 불안정 정렬
- O(NlogN) 시간 복잡도를 가진다
- 맨 오른쪽 또는 맨 왼쪽에 피벗(pivot)을 두고 정렬을 진행한다
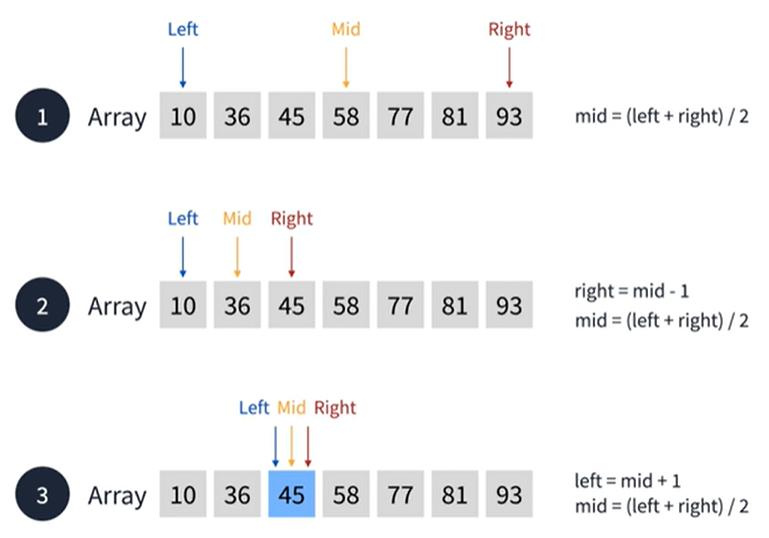
이진 탐색 (Binary Search)
- 정렬 되어 있는 요소들을 반씩 제외하며 찾는 알고리즘
- O(logN) 시간 복잡도를 가진다

이진 탐색의 특징
- 반드시 정렬이 되어있어야 사용할 수 있다
- 배열 혹은 이진 트리를 이용하여 구현할 수 있다
- O(logN) 시간복잡도인만큼 상당히 빠르다
배열을 이용한 이진 탐색 ( 45를 찾아라 )
이진 탐색 트리
- 이진 탐색을 위한 이진 트리로 왼쪽 서브 트리는 루트보다 작은 값이 모여있고 오른쪽 서브 트리는 루트보다 큰 값이 모여있다
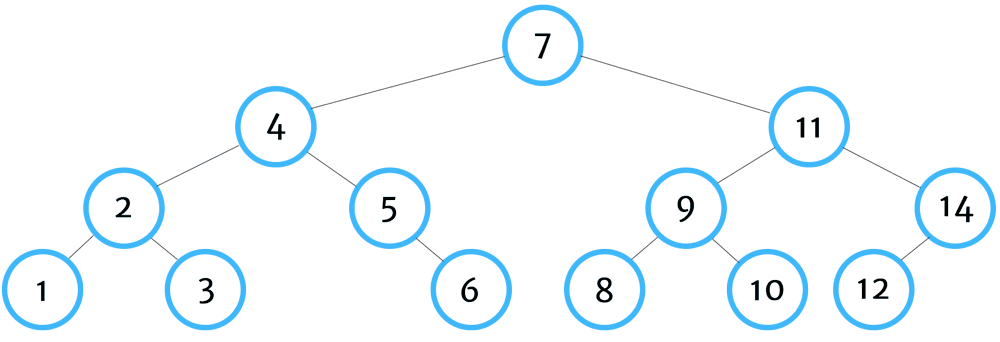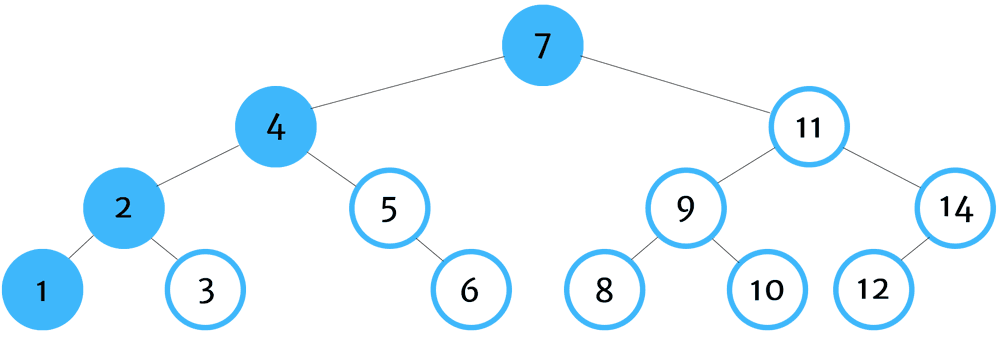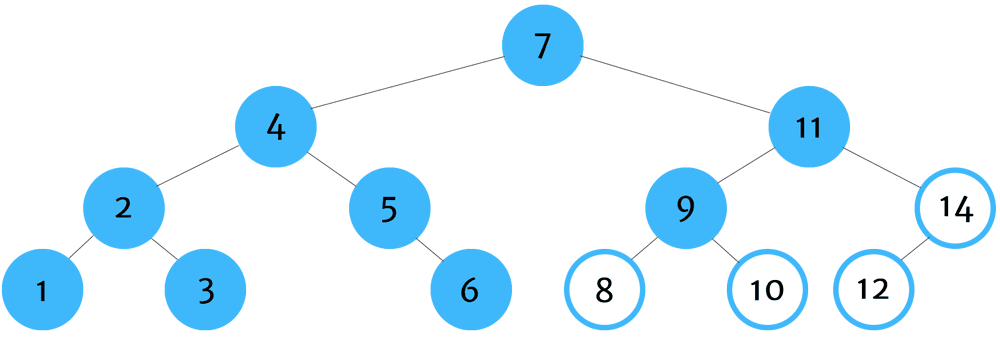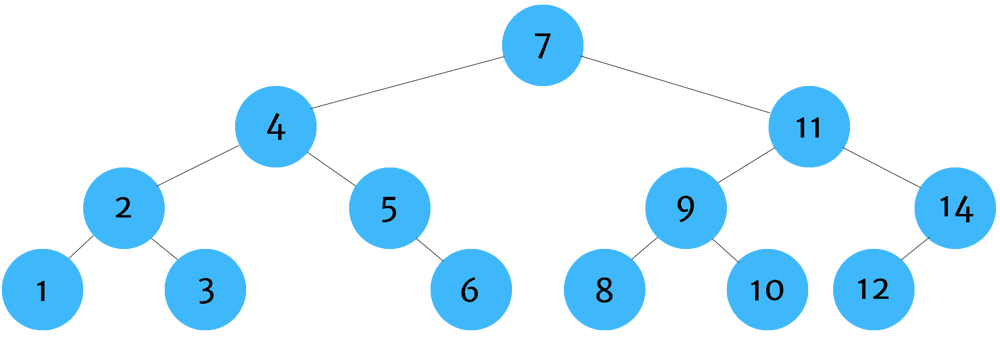
이진 탐색 요소 추가
이진 탐색 요소 제거
1. 단말 정점을 삭제하는 경우
- 별다른 처리 없이 부모 정점과의 연결을 끊으면 된다
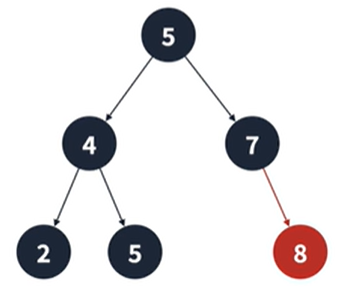
2. 하나의 서브 트리를 가지는 경우
- 제거되는 정점의 부모 간선을 자식 정점을 가르키게 바꾸면 된다

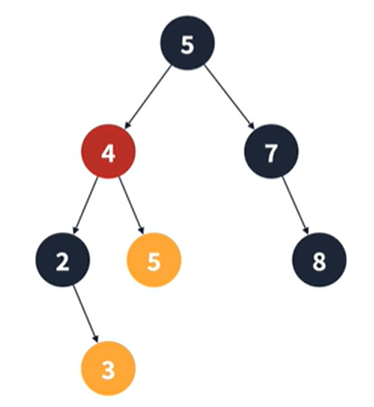
3. 두 개의 서브 트리를 가지는 경우
- 왼쪽 서브 트리의 가장 큰 값 혹은 오른쪽 서브 트리의 가장 작은 값과 교체하면 된다
- 이 경우 교체된 정점의 좌우 자식이 없다면 제거되는 정점의 링크로 대체된다
이진 탐색 트리의 문제점
- 최악의 경우 한쪽으로 편향된 트리가 될 수 있다
- 그런 경우 순차 탐색과 동일한 시간복잡도를 가진다
- AVL 트리, 레드 - 블랙 트리를 이용하면 이진 탐색 트리의 균형을 맞춰줄 수 있다
이진 탐색 구현
const array = [1, 1, 5, 134, 400, 599, 1004, 2876, 8712];
function binarySearch(array, findValue){
let left = 0;
let right = array.length - 1;
let mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
while(left < right){
if(array[mid] === findValue)
return mid;
if(array[mid] < findValue)
left = mid + 1;
else
right = mid - 1;
mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
}
return -1;
}이진 탐색 트리 구현
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
return;
}
let currentNode = this.root;
while (currentNode !== null) {
if (currentNode.value < value) {
if (currentNode.right === null) {
currentNode.right = new Node;
break;
}
currentNode = currentNode.right;
} else {
if (currentNode.left === null) {
currentNode.left = newNode;
break;
}
currentNode = currentNode.left;
}
}
}
has(value) {
let currentNode = this.root;
while (currentNode !== null) {
if (currentNode.value === value) {
return true;
}
if (currentNode.value < value) {
currentNode = currentNode.right;
} else {
currentNode = currentNode.left;
}
}
return false;
}
}